Trap: using memcmp in float type
October 22, 2017
C/C++
Troubleshooting
前言
在一次寫平行程式的過程中,遇到一個很特別的 testcase,是關於 +0.0 & -0.0。
Compare 2 pointer array
當我們要比較兩個大小相同的 array 是否相同,直覺的做法就是 trace 過兩個 array 直接比較數值:
// return 0, same
// return -1, different
int CompareArrays(float* a, float* b, int sz) {
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++){
if (a[i] != b[i]) return -1;
}
return 0;
}
Compare 2 pointer array using memcmp
另一個做法是直接比較記憶體的內容是否相同,就是利用 memory 的角度比較:
// return 0: the contents of both memory blocks are equal
int memcmp ( const void * ptr1, const void * ptr2, size_t num );
理論上這個做法可行,但是今天牽扯到 float 的時候,就要特別注意:
- 浮點數的編碼是根據 IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic IEEE 754
+0.0與-0.0即使在數值上是相同的,但是在編碼上(memory view)是不同值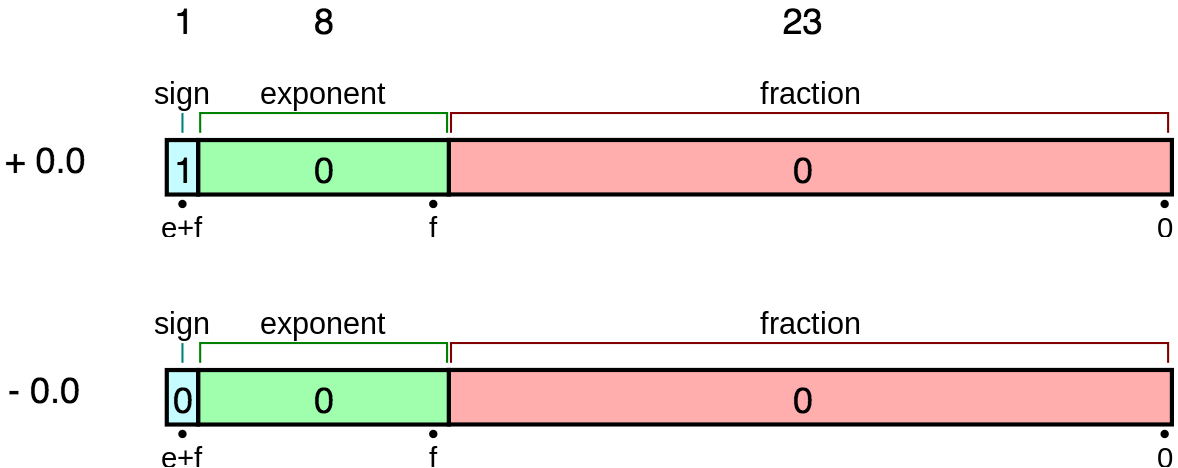
base source
Performance
memcmp 的效率比 loop compare 高太多了
$ ./test 100000000
------ TIMNING -----
[cmpare] 0.390000000
[memcmp] 0.000000000
$ ./test 10000000000
------ TIMNING -----
[cmpare] 5.580000000
[memcmp] 0.000000000
- 在 C standard libraries,視為 built-in
- 被時作成 assembly code 執行
- 針對不同的 CPU Instruction Set 執行對應 Optimized code 參考
Conclusion
因此在 float 的情形下,另外寫一個 compare function 是較好的做法。但是如果情況允許,用 memcmp 的效能會好很多。